Interpolation, extrapolation
Interpolation
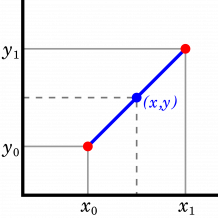
Interpolation is a type of estimation, a function that allow to estimate the value (x, y) between two known data points (x1, y1 ; x2, y2).
A common interpolation method used on ECU is the linear interpolation. The interpolation is more precise on high resolutions maps (multiples points)
Linear interpolation
The formula :
where:
- x1, y1 are the first known coordinates
- x2, y2 are the second known coordinates
- x is the point with want at which we do the interpolation
- y is the interpolated value
Using linear interpolation on 3D maps:
- Interpolate the row above and below
- Interpolate the two interpolated values together
Here is a example, consider the following map:
| Example map (load, engine speed) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Load /RPM | 100 | 150 |
| 1000 | 10 | 20 |
| 2000 | 20 | 40 |
To get the value at load : 125 and engine speed : 1500, we will need to do a linear interpolation since it is not in the map.
The table would look like this after step 1:
| Example map (load, engine speed) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Load /RPM | 100 | 125 | 150 |
| 1000 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| 2000 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
Now we interpolate 15 and 30 together to get the value at 1500 rpm (step 2):
| Example map (load, engine speed) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Load /RPM | 100 | 125 | 150 |
| 1000 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| 1500 | 22.5 | ||
| 2000 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
At load : 125 and engine speed at 1500, we get the value 22.5 with linear interpolation
Extrapolation
ECU does not work with extrapolation. Extrapolation is a an estimation of values that are outside the scope of a map data. There are multiple proposed methods for extrapolation : linear, polynomial, conic, etc.
Extrapolation is not reliable and need to be used with care (if used).