Immobilizer Removal: Difference between revisions
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
'''If you wish to make your own harness you can find the pinout here: [https://the07k.wiki/index.php?title=Reading_and_writing_ECU#Boot_mode ME7.1.1 Pinout], [[:File:OBD2 Pinout.png|OBD2 Pinout]]''' | '''If you wish to make your own harness you can find the pinout here: [https://the07k.wiki/index.php?title=Reading_and_writing_ECU#Boot_mode ME7.1.1 Pinout], [[:File:OBD2 Pinout.png|OBD2 Pinout]]''' | ||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="max-width:500px; overflow:auto;"> | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="max-width:500px; overflow:auto;"> | ||
<div style="font-weight:bold;line-height:1.6;">Bench setup example</div> | <div style="font-weight:bold;line-height:1.6;">Bench setup example</div> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
==== Powering up the ECU in boot mode ==== | ==== Powering up the ECU in boot mode ==== | ||
{{Note|note-reminder|This process can take multiple times before you get the ecu to boot in boot mode}} | {{Note|note-reminder|This process can take multiple times before you get the ecu to boot in boot mode}} | ||
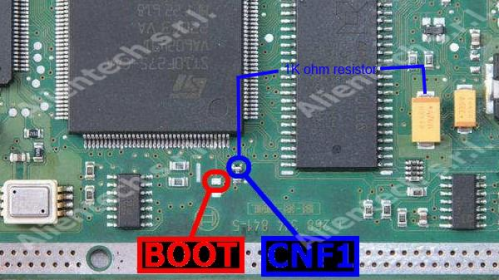
[[File:Boot mode with resistor.png|frameless|499x499px]] | [[File:Boot mode with resistor.png|frameless|499x499px]] | ||
# Before powering up the ECU, you need to ground the '''boot''' pin and put your resistor as shown above | # Before powering up the ECU, you need to ground the '''boot''' pin and put your resistor as shown above | ||
# Now you can power up the ecu, wait about 2 seconds and remove the resistor | # Now you can power up the ecu, wait about 2 seconds and remove the resistor | ||
# The ecu should now be in boot mode (I noticed that the ecu generally runs under 300mA when in boot mode, if you see higher amperage, it's probably not in boot mode) | |||
# The ecu should now be in boot mode (I noticed that the ecu generally runs | |||
=== Using ME7EEPROM to read / write === | === Using ME7EEPROM to read / write === | ||
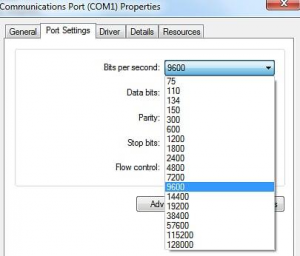
[[File:Port settings.png|thumb|Port settings]] | [[File:Port settings.png|thumb|Port settings]] | ||
==== COM port settings ==== | ==== COM port settings ==== | ||
# On your ''Windows'', open the '''Device manager''' | # On your ''Windows'', open the '''Device manager''' | ||
# Go into '''Communications ports''', find the device that correspond to your cable. | # Go into '''Communications ports''', find the device that correspond to your cable. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 45: | ||
<code>ME7EEPROM_st10.exe -p 1 –b 57600 –bootmode 95160 –r immo_on.bin –CSpin P6.3</code> | <code>ME7EEPROM_st10.exe -p 1 –b 57600 –bootmode 95160 –r immo_on.bin –CSpin P6.3</code> | ||
* '''-p :''' Your COM port | * '''-p :''' Your COM port | ||
* '''-b :''' baudrate, we set it previously to 57600 | * '''-b :''' baudrate, we set it previously to 57600 | ||
| Line 58: | Line 50: | ||
* '''-r :''' Read the EEPROM and save it into the filename immo_on.bin | * '''-r :''' Read the EEPROM and save it into the filename immo_on.bin | ||
* '''--CSpin :''' Keep it a P6.3. Most ME7 ecu use P4.7, but for our specific ME7 with a ST10F microcontroller, it uses P6.3 | * '''--CSpin :''' Keep it a P6.3. Most ME7 ecu use P4.7, but for our specific ME7 with a ST10F microcontroller, it uses P6.3 | ||
=== Disabling the EEPROM from the file === | === Disabling the EEPROM from the file === | ||
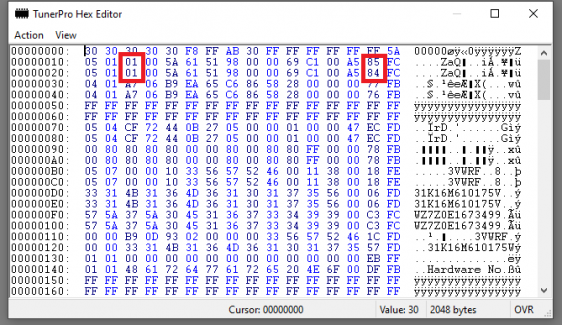
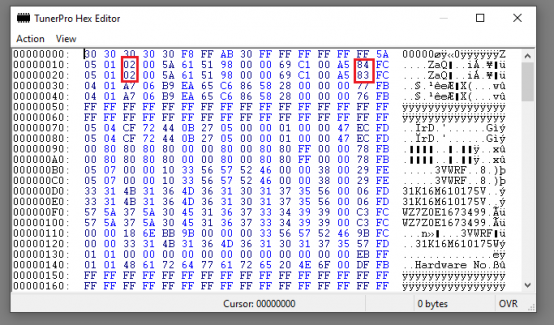
In your hex edit, open the file '''immo_on.bin'''. Change the following values (If hex adresses are confusing, refer to the images): | In your hex edit, open the file '''immo_on.bin'''. Change the following values (If hex adresses are confusing, refer to the images): | ||
* At 0012 and 0022, change 01 to '''02''' (This is immobilizer status, 2 = not active) | * At 0012 and 0022, change 01 to '''02''' (This is immobilizer status, 2 = not active) | ||
* At 001E and 002E, remove '''1''' from actual value (These are the checksums) | * At 001E and 002E, remove '''1''' from actual value (These are the checksums) | ||
[[File:Immo on.png|frameless|562x562px]][[File:Immo off.png|frameless|554x554px]] | [[File:Immo on.png|frameless|562x562px]][[File:Immo off.png|frameless|554x554px]] | ||
| Line 72: | Line 61: | ||
<code>ME7EEPROM_st10.exe -p 1 –b 57600 –bootmode 95160 –w immo_off.bin –CSpin P6.3</code> | <code>ME7EEPROM_st10.exe -p 1 –b 57600 –bootmode 95160 –w immo_off.bin –CSpin P6.3</code> | ||
* '''-w :''' Write the file immo_off.bin into the EEPROM | * '''-w :''' Write the file immo_off.bin into the EEPROM | ||
'''The writing process take some take and will indicate "error" at the end. This is normal, you can read back the ecu to confirm the modifications has been applied.''' | '''The writing process take some take and will indicate "error" at the end. This is normal, you can read back the ecu to confirm the modifications has been applied.''' | ||
==ME17.5== | ==ME17.5== | ||
Revision as of 01:25, 10 August 2022
ME7.1.1
To remove the immobilizer, we will need to read the EEPROM
Reading the EEPROM
You will need the following :
- 1K or 2K ohm resistor
- A VAG KKL cable or any cable with a FTDI (FT232) chip
- A power source to supply the ecu on bench
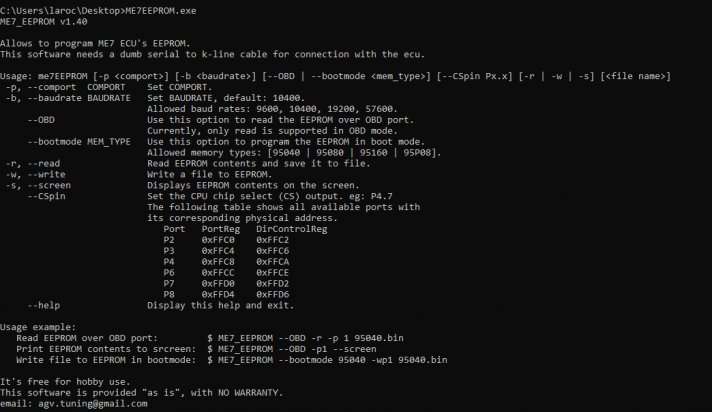
- ME7EEPROM_st10.exe
- A hex editor software (You can use the one from TunerPro)
Open the ecu, you can refer here for instructions : Opening the ecu
To supply power to the ecu off the car, you can make your own harness or use one of these (81 pin ME7 OBD2 Adapater):
If you wish to make your own harness you can find the pinout here: ME7.1.1 Pinout, OBD2 Pinout
Powering up the ECU in boot mode
- Before powering up the ECU, you need to ground the boot pin and put your resistor as shown above
- Now you can power up the ecu, wait about 2 seconds and remove the resistor
- The ecu should now be in boot mode (I noticed that the ecu generally runs under 300mA when in boot mode, if you see higher amperage, it's probably not in boot mode)
Using ME7EEPROM to read / write
COM port settings
- On your Windows, open the Device manager
- Go into Communications ports, find the device that correspond to your cable.
- Double click on it, a properties window should open
- In the Port settings change Bits per second to 57600
- Take note of the COM port number (COM1 would be 1)
Open a terminal (In the search bar, type cmd), go into the directory where ME7EEPROM_st10.exe is located.
To read the EEPROM type in the following command (adapt the parameters for your usage):
ME7EEPROM_st10.exe -p 1 –b 57600 –bootmode 95160 –r immo_on.bin –CSpin P6.3
- -p : Your COM port
- -b : baudrate, we set it previously to 57600
- --bootmode : Required for ME7.1.1 ecu. Equipped with a 95160 EEPROM chipset
- -r : Read the EEPROM and save it into the filename immo_on.bin
- --CSpin : Keep it a P6.3. Most ME7 ecu use P4.7, but for our specific ME7 with a ST10F microcontroller, it uses P6.3
Disabling the EEPROM from the file
In your hex edit, open the file immo_on.bin. Change the following values (If hex adresses are confusing, refer to the images):
- At 0012 and 0022, change 01 to 02 (This is immobilizer status, 2 = not active)
- At 001E and 002E, remove 1 from actual value (These are the checksums)
Save the modified file under the name immo_off.bin. Turn off the ecu, power it back on boot mode.
Using ME7EEPROM_st10.exe, type in the following command to write back the ecu (adapt the parameters for your usage):
ME7EEPROM_st10.exe -p 1 –b 57600 –bootmode 95160 –w immo_off.bin –CSpin P6.3
- -w : Write the file immo_off.bin into the EEPROM
The writing process take some take and will indicate "error" at the end. This is normal, you can read back the ecu to confirm the modifications has been applied.